Barrier to Entry
View FREE Lessons!
Definition of a Barrier to Entry:
A
barrier to entry is an obstacle that impedes potential competitors from entering an industry.
Detailed Explanation:
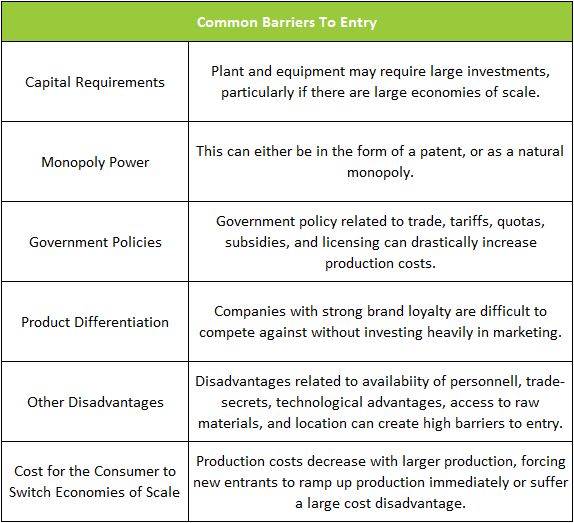
Barriers to entry limit competition. Barriers to entry may be inherent in an industry (natural barriers to entry), or government-imposed (artificial barriers to entry). Every business start-up confronts barriers to entry. Barriers include time and money - items every business must invest in producing a good or service. Governments impose barriers when they create a monopoly by forbidding other companies from entering an industry. In most countries, the government owns the electrical utilities and prohibits companies from competing. At the other extreme are companies with minimal start-up costs and a readily available market. A lemonade stand has few barriers to entry because it requires minimal capital and a readily available market.
High start-up costs are the most common natural barrier to entry. An entrepreneur or company may need to invest a massive sum in a large plant and equipment to start a business or expand into a new product line. The barrier can be enormous when the production process has significant economies of scale, meaning a product’s average cost decreases as output increases. New entrants would operate at a cost disadvantage, making it very difficult to price aggressively until production is sufficient to exploit the economies of scale.
Imagine entering the automobile market. After making the enormous capital investment to manufacture the car, the company would encounter another barrier - developing brand loyalty. It would take years of extensive marketing for customers to accept the viability of a new car manufacturer. It would take even longer to generate the trust and loyalty required to survive. Other barriers include regulatory restrictions, technological advantages, and access to natural resources.
Artificial barriers include barriers imposed by the government. Licensing and educational requirements restrict the number of professionals in many fields. A patent is a government grant that provides inventors the sole right to make and sell their inventions for a set period. The patent can be a barrier to entry if it deters other companies from developing competing products. Government-imposed trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies may be too much of a barrier for a company to conduct business in a country.
High barriers to entry benefit a company already in an industry by discouraging competition. Low barriers to entry foster increased competition by increasing the number of sellers. Entrepreneurs may enter a business if they see another company earning a hefty profit.
High barriers to entry benefit a company already in an industry by discouraging competition. But low barriers foster increased competition by increasing the number of sellers. Entrepreneurs may enter a business if they see another company earning a hefty profit. Technology can break down a barrier. The cell phone and switching technology destroyed large phone company monopolies. The Internet reduced the barriers to entry in many industries. For example, eBay and Amazon broke geographical barriers by opening markets for many entrepreneurs in areas far from home.
Dig Deeper With These Free Lessons:
Entrepreneurs – Their Vital Role in The Economy
Capital – Financing Business GrowthChange in Supply– When Producer Costs Change
Factors of Production – The Required Inputs of Every Business
Supply – The Producer's Perspective
Market Structures I – Perfect Competition and Monopoly
Market Structures II – Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
