Factor Market
View FREE Lessons!
Definition of a Factor Market:
A
factor market is a market where businesses purchase the items needed to produce goods or services. Households sell or provide labor, entrepreneurial talent, capital, land, and natural resources in the factor market.
Detailed Explanation:
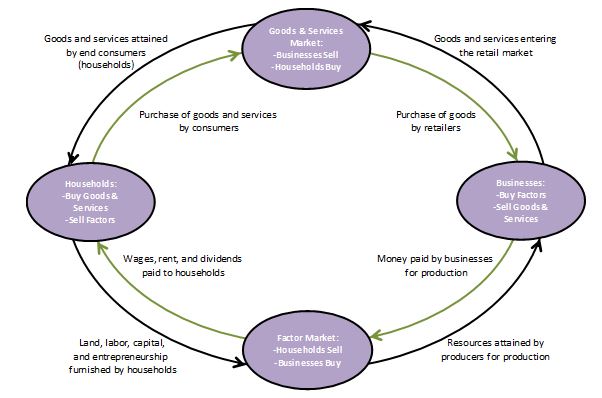
The factor market—sometimes called the input market—is where a business buys its factors of production, which are the resources used to produce the goods or services it sells. They include labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurial talent. The factor market is distinct from the goods and services market, where consumers purchase the final product. For example, a furniture manufacturer acquires its labor, wood, leather, and other materials in the factor market, and sells its furniture to households in the goods and services market. The relationship between the factor market and the goods and services market is best illustrated using the circular flow diagram. Here we see that in the goods and services market, households are buyers, and businesses are sellers. This is reversed in the factor market: households are sellers and businesses are buyers.
Everyone participates in the factor market.
A person seeking employment enters the factor market. Employees are paid a wage through the factor market. Households may also receive dividends or rent from a business as compensation for providing financial capital or real estate which they acquired in the factor market. Even the unemployed can be investors. For example, independently wealthy individuals may enter the factor market as real estate investors and lease a building to a company. The pension fund of a recent retiree earns dividends when investing in companies through the factor market.
The law of supply and demand determines prices in the factor market. However, the demand is "derived" from the demand for the final good or service. If the demand for chairs increases, the manufacturer will hire more workers, and purchase more wood and leather, thereby increasing the demand for the factors of production. The demand for these factors will decrease if the demand for chairs decreases.
Dig Deeper With These Free Lessons:
Factors of Production – The Required Inputs of Every Business
Circular Flow Model – We Depend on Each OtherGross Domestic Product – Measuring An Economy’s
Performance
Supply and Demand – Consumers and Producers Reach Agreement
Entrepreneurs – Their Vital Role in The Economy
Capital and Consumer Goods – How They Influence Productivity